
When this occurs, their intermolecular repulsive forces counteract the attracting forces between the molecules of the surface liquid.DPPC forms a monolayer at the gas-fluid interface, with the hydrophilic heads towards the water and hydrophobic tails towards the gas.Produced by Type II alveolar epithelial cells.
 DPPC is amphipathic (charged choline head, hydrophobic. Surfactant is mainly phospholipid (dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine DPPC), some protein and carbohydrate. T - surface tension along the surface of the sphere. P - distending pressure within the lumen of a sphere. Laplace's Law: P = 4 x T / r (for a sphere). Surfactant dramatically reduces surface tension. High surface tension of liquid lining the alveoli tends to collapse them. Separates abdominal and thoracic contents. Peripheral afferents from intercostal and subcostal nerves. Efferent and central afferent: phrenic nerve (C3-5). Back attaches to T12 vertebral body, descents to L1/L2 on sides. Front arises from xiphoid process, costal margins. 3 Openings: Aorta (T12), oesophagus (T10) and vena caval (T8). Muscle fibres arise from peripheral attachment to form central tendon →Ĭrest of diaphrgam (thin but strong aponeurosis). C- shaped structure of muscle and fibrous tissues.
DPPC is amphipathic (charged choline head, hydrophobic. Surfactant is mainly phospholipid (dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine DPPC), some protein and carbohydrate. T - surface tension along the surface of the sphere. P - distending pressure within the lumen of a sphere. Laplace's Law: P = 4 x T / r (for a sphere). Surfactant dramatically reduces surface tension. High surface tension of liquid lining the alveoli tends to collapse them. Separates abdominal and thoracic contents. Peripheral afferents from intercostal and subcostal nerves. Efferent and central afferent: phrenic nerve (C3-5). Back attaches to T12 vertebral body, descents to L1/L2 on sides. Front arises from xiphoid process, costal margins. 3 Openings: Aorta (T12), oesophagus (T10) and vena caval (T8). Muscle fibres arise from peripheral attachment to form central tendon →Ĭrest of diaphrgam (thin but strong aponeurosis). C- shaped structure of muscle and fibrous tissues. 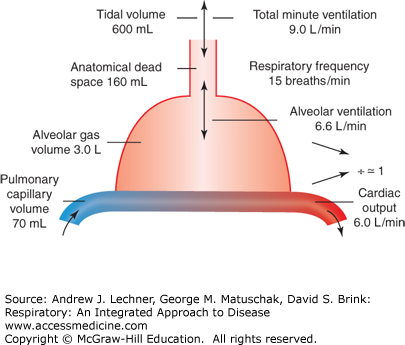
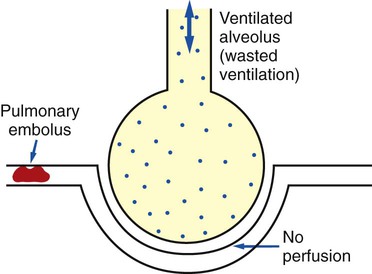
Dome shaped muscle that inserts into the lower ribs.Perfusion vs Diffusion Limited Gas Transfer.Time Dependence of Pulmonary Elastic Behaviour.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
